APQ Optical Design
We are convinced that the new CMOS sensors, in particular, require an innovative optical design that meets the increased image quality requirements.
Visual observers will also benefit from the performance of the newly developed Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromats because in the peripheral regions of the visual spectrum there is no decrease of the Strehl ratio near or below the diffraction limit as is the case with most apochromats.
Below is a detailed presentation of the optical design of the new astronomical objectives, developed by Uwe Laux, Dipl.-Ing. (FH) for technical optics (details on optical design see Laux, Uwe: Astrooptik. Optik-Systeme für die Astronomie. 3rd revised and amended edition, 2017, pp. 146-155 and the related patent application).
- Aim
- Quadruplet
- Strehl
- Blocking
- Professional
- Oil spacing
- AR-Coating
- 150/1200
- Designs
In the course of developing a new generation of astronomical objectives, we quickly realized that the classic apochromatic triplet design can only partially exploit the full UBVRI spectral range (365nm – 1014nm) of modern electronic sensors (CCD, CMOS).
The aim for the new generation of objectives was therefore to create a design that reproduces (as far as possible) without errors in this broad spectral range. For this purpose, several conditions must be met.
Continue readingIn a state of the art triplet apochromat, the particularly annoying Gaussian error is not correctable.
Only when the sine or isoplanase condition is satisfied, does an optical system imagine properly. Such an objective is also referred to as an aplanatic (error-free) objective.
The polychromatic image quality is not artificially changed or "nicely calculated", as this would not improve the optical correction. Instead, the optical system is optimized in the spectral range from 365nm to 1014nm by means of a wavelength table and the respective weighting factors of 1.
The result of the optimizations is a four lens polychromatic basic system in which the CaF₂ lens is protected between two lenses made of special optical glasses.
The quadruplet lens design of the polychromatic objective is particularly suitable for larger refractors from about 130mm aperture. Here the color longitudinal and the Gaussian error can be optimally corrected.
Continue readingThe longitudinal chromatic aberration shows the typical course of a polychromatic correction, i.e. the curve has more than 3 points of intersection with the central image plane.
Our goal of a diffraction-limited imaging quality in the form of a Strehl number ≥ 0.9 over a spectral range from 365nm (UV) to 1014nm (IR) is fully achieved by this innovative optical design.
The new optical system and design was registered as patent by us under the name Polychromatisches Objektiv und Verfahren zum Entwurf eines polychromatischen Objektivs, file number 10 2016 123 732.9, at the German Patent and Trademark Office (DPMA).
With visual observations and CCD imaging, an almost error-free image is guaranteed. The images are bright, virtually free of chromatic aberrations, astigmatism, coma, aperture and Gaussian errors; the theoretical resolution is almost reached.
Especially in the demanding planetary observation highest magnifications are possible due to the brilliant, detailed and high-contrast image quality; the optical superiority over conventional apochromatic systems becomes clear.
In the peripheral regions of the visual spectrum there is no decrease of the Strehl ratio near or below the diffraction limit as is the case with most apochromats, as illustrated by the following normalization of the spectral range from 436nm to 707nm:
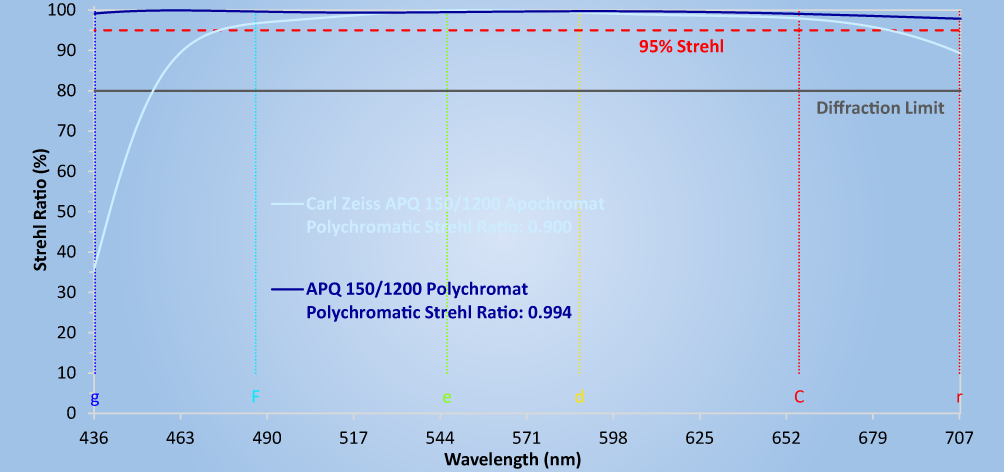
The extreme imaging quality of the four lens polychromat as a basic system enables the combination of field correctors and focal length changing systems such as Barlow systems and reducer correctors.
The usable wavelength range is 365nm to 1014nm and thus up to three times wider compared to the limited visual spectral range of classic apochromatic doublet and triplet lenses (usually 436nm – 656nm and 480nm – 707nm, respectively).
As a result, our customers gain large proportions of the usable UBVRI spectral range of modern CCD and CMOS sensors with their large image diagonals, pixel numbers and high quantum efficiency in both UV and IR.
It is noteworthy that the useful wavelength range of the new Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat is almost identical to those of the CCD and CMOS sensors.
This opens up completely new areas of research and activity. Hitherto unobservable structures in the UV and IR become visible.
Apochromatic fluorophosphate and CaF₂ doublet and triplet lenses are dependent on UV/IR blocking filters to suppress the UV/IR spectrum.
Since these apochromats are designed only for the visual spectral range, usually the "disturbing" spectral components must be filtered out in order to obtain a sufficiently sharp image.
Continue readingIn contrast, when using Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromats, the application of such UV/IR blocking filters is not only superfluous, but even counterproductive, because essential spectral information of the object is lost.
From the quadruplet basic lens design, polychromats with extreme focal ratios from f/1 to f/8 can be derived, by adding additional lenses, replacement of fluid, optically transparent media, by air gaps or the execution of glass-air surfaces as aspheres and by substitution of the optical glasses by crystalline and special media.
Continue readingThese special polychromats are used e.g. as astrographs and other systems with a usable spectral range from 320nm to 2500nm. Such instruments include special Echelle spectrographs, focal reducers and camera systems of modern professional astronomy.
The assembly technology used by means of a fluid, optically transparent medium (oil) between the lenses offers several advantages over the classical technology of the individual lenses with air gaps:
Thermal stresses between the lenses are excluded by the oil in between.
The oil film prevents surface tilting, as is possible with an air gap.
Continue readingThere are fewer glass-to-air surfaces and thus virtually no stray light, the transparency of the optical system increases.
The adaptation to the ambient temperature is faster, i.e. the optical system has a better thermal behavior.
Conventional anti-reflection coatings (AR coatings) do not match the high optical imaging properties of the polychromatic objectives, as they are usually optimized for the visual spectral range only.
Therefore we have developed a completely new ultra broad band AR coating for the Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromats, characterized by an extremely low residual reflectivity RAVG of < 0.7% over the entire spectral range from 365nm (UV) to 1014nm (IR).
The four lens design of the polychromat with only two glass-to-air surfaces (version with an asphere without air gaps) on the outer sides together with the innovative ultra broad band AR coating reduces residual reflections to the physical minimum.
Continue readingThe interaction of the CaF₂ with its high transmission over a wide spectral range from UV to IR with the oil-immersion technology without air gaps leads to a further increase in the transparency of the optical system and extremely sharp images without reflections.
The currently available AR coating technology limits the spectral range usable in practice to 365nm to 1014nm.
Optionally, special UV or IR AR coatings can be offered for special applications.
A Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat can be realized in different versions. On the individual execution options can not be discussed in detail here. Reference is made to the relevant patent application.
Our design variant presented here, a completely oil spaced APQ 150/1200 Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat with an asphere, with 150mm aperture and 1200mm focal length, conforms to that of the first manufactured prototypes.
The progression of the Strehl ratio as a function of the wavelength on the one hand shows that the value of ≥ 0.9 is not only achieved in the spectral range from 365nm (UV) to 1014nm (IR).
On the other hand, it also becomes clear that there is a very good polychromatic correction from the ultraviolet to the infrared region of the spectrum, so that this four lens objective is diffraction-limited from 365nm to at least 1365nm.
The theoretically usable wavelength range of this quadruplet polychromatic objective is over 1000nm and is thus three to four times wider than the conventional doublet and triplet apochromats.
In practice, currently available AR coating technology limits the usable spectral range to 365nm to 1014nm.
Continue readingIn the wavelength range from 365nm to 1365nm, the APQ 150/1200 Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat with an asphere has a polychromatic Strehl ratio of 0.988 and a maximum focal shift range of ±0.007%:
From 365nm to 1014nm the polychromatic Strehl ratio is 0.988 and the maximum focal shift range is ±0.003%.
With the production of the first two prototypes of the oil spaced APQ 150/1200 Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat with an asphere, 150mm aperture and 1200mm focal length, we set ourselves a very demanding goal.
The four lens design – with or without asphere, completely oil spaced, with or without air gaps, with focal ratios from f/5.6 (f/3.9 with reducer corrector 0.7x) to f/15 (as a replacement for the objective of the Coudé refractor AS 150/2250) – offers a huge potential for all kinds of visual and photographic observation.
After providing practical proof of feasibility with the first prototypes of the APQ 150/1200 Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat, we will continue to expand our portfolio.
This goal includes both smaller, but especially larger apertures, where customers have the choice of the focal ratio and the anti-reflection coating, if feasible.
The following table presents some possible designs of the Fluorite Quadruplet Polychromat, where in the spectral range from 365nm to 1014nm a polychromatic Strehl ratio > 0.95 and a large focal ratio is achieved.
(mm)
(mm)
(%)
1 D…Aperture
2 f…Focal length
3 D/f…Focal ratio
4 Sp…Polychromatic Strehl ratio
5 LCA…Maximum focal shift range



